Company Snapshot: Sony Group Corporation (TYO: 6758)
Scaling Entertainment and IP While Unlocking Cross-Business Synergies
Hi guys,
This week’s article is on Sony, the Japanese entertainment powerhouse behind the famous Playstation brand. Have a good weekend ahead.
Business Overview
Sony Group Corporation was founded in Japan in May 1946 as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha. Over the decades, it transformed from an electronics manufacturer into a global entertainment and technology powerhouse. In September 1970, Sony expanded its global footprint by listing on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
From pioneering personal entertainment with the Walkman and Discman to shaping the future of gaming, film, and music, Sony has left its mark across multiple industries. Today, it’s best known for its PlayStation, TVs, audio headphones, digital cameras, movies and music.
But Sony’s reach extends beyond entertainment and consumer electronics. It has also ventured into insurance, banking, electric vehicles, and medical imaging. Though it has exited some of these industries, Sony once produced batteries, chemicals, and PCs, even playing a key role in lithium-ion battery innovation before shifting focus.
Today, Sony operates across several seven business segments, including:
Games and Network Services
Music
Pictures
Entertainment, Technology & Services
Imaging & Sensing Solutions
Financial Services
All Other
1. Games and Network Services (“G&NS”)
Sony undertakes product research, development, design, marketing, sales, production, distribution and customer service for PlayStation hardware, software, content and network services. The G&NS segment is divided into three key areas:
Digital Software and Add-on Content: Distribution of software titles and add-on content through the network by Sony Interactive Entertainment;
Network Services: Network services relating to game, video and music content; and
Hardware and Others categories: Home gaming consoles, packaged software, game software sold bundled with home gaming consoles, peripheral devices and first-party software for third-party platforms.
2. Music
Sony’s music segment is divided into three areas:
Recorded Music: Covers both physical and digital music distribution, as well as revenue from artists’ live performances. Sony Music Entertainment (SME) operates globally (excluding Japan), focusing on developing, producing, marketing, and distributing music across all formats and genres. Meanwhile, Sony Music Entertainment Japan (SMEJ) handles the Japanese domestic market, producing recorded music and music videos in partnership with artists across various genres;
Music Publishing: Manages and licenses song lyrics and compositions. Sony Music Publishing (SMP), based in the U.S., owns, administers, and acquires rights to musical works. It markets and licenses these compositions to generate royalties and fees from their use; and
Visual Media and Platform: Covers animation production and distribution, game applications, and services for music and visual products.
3. Pictures
Motion Pictures: Covers the production, acquisition, and global distribution of both live-action and animated films. Its major production studios include Columbia Pictures, Screen Gems, TriStar Pictures, 3000 Pictures, Sony Pictures Animation, Stage 6 Films, AFFIRM Films, and Sony Pictures Classics. Sony also operates Sony Pictures Imageworks, a leading visual effects and animation studio, and Sony Pictures Studios, which houses post-production facilities;
Television Productions: Focuses on the production, acquisition, and distribution of TV programming worldwide. It includes everything from scripted series, reality shows, daytime serials, game shows, animated series, TV movies, and miniseries;
Media Networks: Runs TV channels and direct-to-consumer (DTC) streaming services worldwide. This includes:
SPNI (Sony Pictures Networks India) – Operates TV channels across India;
Game Show Network (GSN) – A U.S.-based network available on cable, satellite, and other platforms;
Crunchyroll – A leading anime-focused streaming service in North America;
SonyLIV – A general entertainment streaming service in India.
4. Entertainment, Technology & Services (“ET&S”)
TV & Audio/Video: Sony undertakes product research, development, design, marketing, sales, production, distribution and customer services for televisions and video and audio products;
Still & Video Cameras: Sony is a leader in digital imaging, producing interchangeable lens cameras, compact digital cameras, and professional video cameras. The company handles research, development, manufacturing, and sales, catering to both casual users and professional filmmakers;
Mobile Communications: Sony develops and sells mobile phones, accessories, and applications. It also operates internet broadband network services and provides content distribution through its portal services, making Sony devices more connected across PCs, mobile phones, and other electronic platforms.
5. Imaging & Sensing Solutions (“I&SS”)
This segment handles the research, development, design, manufacturing, marketing, and sales of complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensors, along with other semiconductor-related products like display devices, lasers, and large-scale integration systems (LSIs). Sony’s CMOS image sensors are widely used in smartphones, but they also power digital cameras, security cameras, factory automation systems, and automotive applications.
6. Financial Services
Sony Financial Group Inc. (SFGI) operates insurance, banking, and financial services primarily through:
Sony Life – A Japanese life insurance company.
Sony Assurance – A Japanese non-life insurance company.
Sony Bank – A Japanese internet-based bank.
All three are wholly owned by SFGI and serve as Sony’s key financial businesses.
7. All Other
This segment includes various business operations outside Sony’s core industries, such as disc manufacturing (outside Japan) and recording media and storage solutions.
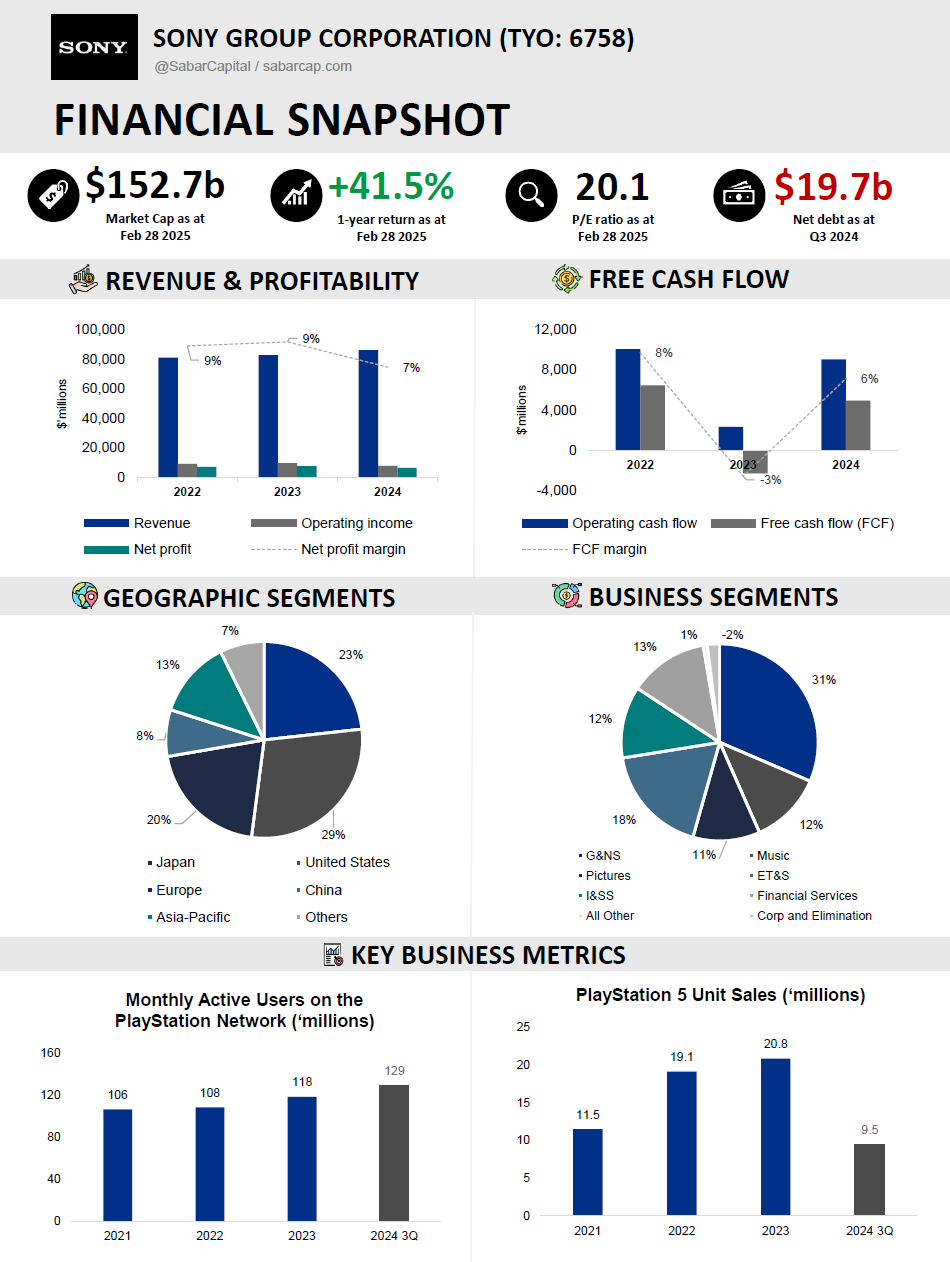
Sony operates a well-balanced and profitable portfolio across multiple business segments, with G&NS (31%) as the largest contributor, followed by ET&S (18%), Financial Services (13%), Music (12%), I&SS (12%), and Pictures (11%). Each segment is generating profits, showcasing Sony’s operational strength and resilience across industries.
Geographically, Sony maintains a strong global presence, with its largest markets being the U.S. (29%), Japan (23%), and Europe (20%). The Asia-Pacific region (excluding China) contributes 13%, while China alone accounts for 8%, and other regions make up the remaining 7%. This well-distributed revenue base helps Sony mitigate regional risks while capitalizing on opportunities across multiple.
Competitive Landscape
Strong brand with market leadership
Sony is a globally recognized brand in entertainment, gaming, and technology, with a strong presence across PlayStation, TVs, music, film, and digital cameras. It has successfully positioned itself as a premium brand, leading in multiple industries.
G&NS
Sony continues to dominate the gaming industry through its PlayStation ecosystem, which remains a market leader in both hardware and software. The PS5 has significantly outsold the Xbox Series X/S, with estimated November 2024 sales reaching 4.12 million units, compared to 0.77 million for Xbox Series X/S. As of January 2025, over its lifetime, PS5 sales have hit 67.7 million, more than double Xbox’s 31.2 million. This success is driven by PlayStation Studios' first-party games, including globally renowned franchises like The Last of Us, God of War, and Spider-Man. These exclusive titles continue to be a key differentiator, reinforcing PlayStation’s dominance in the gaming market.
Pictures
Sony Pictures Entertainment (SPE) holds a unique position as the only major independent Hollywood studio, giving it flexibility in distribution and partnerships. The studio manages a rich content library, including over 4,000 movie titles and 400 TV series, making it a key player in film and television production.
In television, Sony Pictures Television (SPT) is producing major streaming hits, demonstrating its growing influence in the industry. The Night Agent became Netflix’s most-watched TV series in 2023, while Dark Matter debuted as the top show on Apple TV+ worldwide in 2024. This success highlights Sony’s ability to create and distribute premium content across multiple streaming platforms.
Sony also dominates the anime industry through Crunchyroll, which surpassed 15 million paid subscribers as of July 2024. The platform continues to expand its anime offerings while growing its experiential entertainment initiatives, further strengthening Sony’s foothold in this fast-growing segment.
Music
Sony is a dominant force in the music industry through Sony Music Publishing (SMP) and Sony Music Entertainment (SME). SMP holds the #1 position in the global music publishing market, while SME ranks #2 in recorded music worldwide, showcasing Sony’s influence across the industry.
Sony’s music catalog has seen significant growth, now managing 6.24 million copyrighted songs as of March 31, 2024, a 1.7x increase over the past decade. The company’s streaming business is rapidly expanding, with streaming revenue from recorded music and publishing growing 19% y/y. This reflects Sony’s ability to adapt to the digital music era and leverage streaming as a key growth driver.
SMP’s songwriters played a crucial role in global hits, contributing to #1 songs in 37 out of 52 weeks on the Weekly Spotify Worldwide Chart in 2023. Additionally, Sony’s share of new songs in the U.S. has increased for five consecutive years, reinforcing its influence over the modern music landscape. The company continues to expand its streaming catalog, with the number of new tracks released on digital platforms growing 24% compared to FY2019.
I&SS
Sony is the undisputed leader in CMOS image sensors, holding a 53% global market share in 2023, with a target to expand to 60% by 2025. Its cutting-edge sensor technology powers some of the world’s most advanced imaging systems, making it a crucial supplier in the consumer electronics and industrial imaging sectors.
Sony’s image sensors have experienced continuous growth since the 2010s, primarily driven by mobile devices. The company leads the shift toward larger, high-performance sensors, improving image quality, resolution, and low-light performance. As smartphone manufacturers continue to demand cutting-edge imaging solutions, Sony aims to further expand its market share through continued technological innovation and industry partnerships.
Beyond mobile, Sony is aggressively expanding in the automotive image sensor market, targeting a 43% market share by FY2026. With the rise of autonomous driving and ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), demand for high-sensitivity, low-noise, and AI-enhanced sensors is increasing. Sony’s imaging solutions are being integrated into self-driving car systems, in-vehicle monitoring, and smart transportation technologies, helping enhance safety and automation.
Sony is a known supplier of image sensors for Apple, powering the cameras in iPhones with high-performance CMOS sensors that improve low-light capabilities, dynamic range, and autofocus speed. This partnership underscores Sony’s position as the go-to provider of premium imaging technology for the world’s top smartphone brands.
Sony’s advanced CMOS image sensor technology is built on industry-leading expertise in pixel design, signal processing, and AI-driven algorithms. These sensors deliver:
High sensitivity and low noise for superior image clarity
Wide dynamic range and high-speed image capture for real-time applications.
Low power consumption for efficient use across mobile, automotive, and industrial applications.
Sony is also expanding its sensor applications into industrial and retail AI-powered solutions, integrating edge AI processing for logistics, security, and smart automation.
Sony continues to push boundaries with Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR), becoming the first company in the world to mass-produce semiconductor lasers—a key component for HAMR—through a partnership with Seagate Technology. This breakthrough will significantly enhance storage capacity and efficiency in next-generation data storage systems. Additionally, Sony is advancing its AITRIOS™ Edge AI Sensing Platform, which integrates AI-driven image sensing technology for smart automation across retail, logistics, and industrial sectors.
Diversified Business Portfolio
Sony's competitive edge lies in its remarkably diversified portfolio, spanning multiple business segments and geographic markets. The company isn’t dependent on just one industry — its revenue comes from robust divisions like G&NS, Film, Music, ET&S, I&SS, and Financial Services, all of which consistently post profits. This diversified approach not only buffers Sony against market fluctuations in any single sector but also enables cross-promotional synergies among its varied operations.
On the geographic front, Sony has a strong global footprint with significant revenue coming from the U.S., Japan, Europe, and rapidly growing markets in the Asia-Pacific region and China. This global spread reduces dependency on any single region, allowing Sony to tap into diverse consumer bases and adapt to different economic conditions worldwide. Together, these strategic advantages provide Sony with resilience, agility, and a broad platform for sustainable growth and innovation.
Cross-Segment Synergy
One potentially underrated aspect of Sony’s business lies in its highly diversified yet interconnected business segments, allowing the company to leverage its strengths across gaming, film, music, semiconductors, and entertainment technology. Unlike competitors that focus on a single industry, Sony creates a self-reinforcing ecosystem where success in one segment fuels growth in another. PlayStation franchises evolve into blockbuster movies, Sony Music artists feature in films and game soundtracks, and cutting-edge image sensor technology enhances gaming accessories.
One of Sony’s biggest strengths is its ability to leverage its vast portfolio of intellectual property (IP) across multiple industries, including gaming, film, music, and technology. This interconnected ecosystem allows Sony to monetize its franchises in multiple ways, including movies, TV series, gaming adaptations, and merchandising. By integrating its businesses, Sony creates a self-reinforcing cycle where success in one segment drives growth in others. This cross-segment synergy not only strengthens Sony’s market position but also unlocks multiple revenue streams and drives operational efficiencies across industries, ensuring long-term growth, cost optimization, and resilience in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Gaming Meets Film & TV
Sony has successfully translated its PlayStation franchises into major Hollywood productions, expanding their reach beyond gaming audiences. The Last of Us (HBO, 2023), based on Naughty Dog’s best-selling game, became a massive hit, proving that high-quality storytelling from PlayStation Studios can thrive in television.
Similarly, upcoming projects like the Ghost of Tsushima movie and the Horizon Zero Dawn Netflix series will bring more PlayStation franchises to mainstream audiences. Sony has also capitalized on its racing game franchise with Gran Turismo (2023), which demonstrated the potential for adapting non-traditional gaming IP into compelling films.
This cross-segment collaboration benefits Sony Pictures by providing it with proven, built-in audiences from gaming, ensuring box office and streaming success. PlayStation Studios works closely with Sony Pictures to maintain the integrity of these adaptations, ensuring that the high storytelling standards set by the games translate well into film and TV.
Sony Music & PlayStation: Cross-Promotion Through Soundtracks
Sony’s music division plays a crucial role in its entertainment ecosystem, supplying soundtracks for both Sony Pictures films and PlayStation games. For example, the soundtrack for Spider-Man: Across the Spider-Verse (2023) was released under Sony Music, boosting both the movie’s brand and Sony’s artists. Similarly, the Uncharted (2022) movie featured Sony Music artists, showcasing how Sony leverages its music catalog across different entertainment platforms.
Even within gaming, PlayStation franchises frequently incorporate Sony Music artists into their soundtracks — a prime example being The Last of Us, which features original compositions from Sony’s music catalog. This cross-promotion strategy strengthens Sony’s ecosystem, ensuring that its films, games, and music continuously feed into one another.
Gaming Technology & Image Sensors
Sony’s image sensor division plays a key role in gaming innovations, supplying advanced CMOS image sensors for PlayStation’s hardware. PlayStation VR2 (PSVR2) relies on Sony’s high-end image sensors for motion tracking, enhancing the immersive gaming experience. Likewise, the PlayStation Camera incorporate Sony’s imaging technology, showcasing how Sony’s gaming division benefits from its R&D.
Game Engine Technology Revolutionizing Virtual Production
Sony’s cross-segment synergy extends into virtual production, combining its expertise in film, gaming, and imaging technology to push the boundaries of content creation. A key part of this strategy involves Epic Games' Unreal Engine, a leading real-time 3D creation tool widely used in both gaming and film production. Sony holds a minority stake in Epic Games, reinforcing its commitment to advancing real-time graphics technology and interactive media.
Through Pixomondo and Sony PCL, Sony provides virtual production services that utilize large LED screens to display real-time digital backgrounds, allowing physical subjects and virtual environments to interact seamlessly while being shot simultaneously. This technology eliminates the constraints of physical shooting locations and enhances the efficiency, flexibility, and creative possibilities of modern filmmaking.
Maximizing Film IP Through Location-Based Entertainment
Beyond traditional entertainment, Sony Pictures Entertainment (SPE) is expanding into experiential entertainment by monetizing its strong franchises like Jumanji and Ghostbusters through Location-Based Entertainment (LBE). This approach allows Sony to extend its IP beyond the screen, offering theme park-style attractions and interactive experiences.
A major step in this direction was the launch of Wonderverse in January 2024, Sony’s first immersive entertainment destination. By creating physical experiences based on its movie franchises, Sony is diversifying its revenue streams, extending the lifespan of their IP while deepening fan engagement.
Key Financials
Opportunities:
Expanding into new markets: entry into the electric vehicle (EV) industry through Sony Honda Mobility, with the Afeela EV set to launch in 2025.
Expansion in emerging markets:
Music & Entertainment: Sony is increasing revenue opportunities for its music catalog, ensuring a wider global reach.
Japanese Animation & Artists: The company is accelerating global marketing efforts for anime and J-pop, leveraging the growing international demand for Japanese entertainment.
Entertainment and Creation-Focused Strategy
Shift Towards Creation & Kando: Sony is shifting its management focus toward creation and emotional impact ("Kando") in the 21st century. In the past, Sony delivered Kando through innovative products like the Trinitron TV and Walkman; today, it aims to achieve the same through content and entertainment
Spinning off part of the financial segment in 2025 to focus more on entertainment and content creation
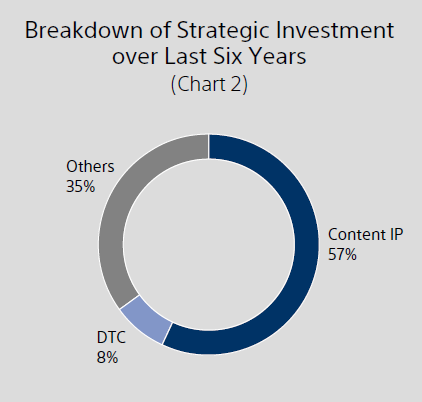
Investment in Content: Sony has invested approximately 1.5 trillion yen over the past six years to strengthen content creation. Content IP accounts for 57% of Sony’s total 2.4 trillion yen strategic investment, reflecting the company's long-term commitment to entertainment. Including music catalog acquisitions and other expenses, Sony’s total investment in content IP stands at roughly 1.5 trillion yen over six years
Growth in Entertainment Businesses: Entertainment segments (Games & Network Services, Music, and Pictures) now account for 60% of Sony’s total sales. The proportion of Sony’s total sales from entertainment has grown from 26% in FY2012 to 55% in FY2023.
Strategic Investments & Acquisitions: Sony continues to strategically invest in content IP and direct-to-consumer (DTC) services. This includes acquiring companies with strong IP assets and investing in IP development & production studios to strengthen its position in the entertainment industry.
Risks:
Rapid Technological Changes: The entertainment industry is evolving rapidly, with streaming, digital distribution, and AI-driven content creation reshaping business models (e.g. cloud gaming and live-service models)
Intensifying Competition in Gaming: Sony dominates the gaming industry with PlayStation, but competition is heating up from Microsoft, Nintendo, and emerging Chinese AAA developers. Xbox Game Pass is a major threat, as Microsoft aggressively expands its subscription and cloud gaming model, while Sony lags in cloud gaming infrastructure. Nintendo remains strong in family-friendly and handheld gaming, maintaining a loyal player base despite Sony’s technological edge. Chinese AAA studios are closing the quality gap, with high-budget, visually stunning games like Black Myth: Wukong (Game Science) and Where Winds Meet (Everstone Studio) challenging Western AAA dominance. State-backed funding gives Chinese studios an edge, allowing them to scale quickly and take risks, while Western studios struggle with massive budgets and long development cycles. Tencent and NetEase are shifting from mobile to premium console and PC games, competing directly with PlayStation Studios.
Film & Music Streaming Challenges: Sony Pictures and Sony Music are strong players in entertainment, but the dominance of streaming platforms presents risks. Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime control global content distribution, limiting Sony Pictures’ ability to own its own platform. Sony lacks a dedicated streaming service, relying on licensing deals that may become less favorable over time. Music streaming (Spotify, Apple Music) lowers profit margins, as these platforms take a significant share of revenue from Sony Music artists and catalogs. Sony may lose pricing power and control over its content, reducing profit margins across its film and music businesses
Conclusion
Sony's diversified business model provides a strong competitive edge and resilience against industry-specific risks. Its leadership in gaming, film, music publishing, and image sensors underscores its market dominance, while strategic investments in content and expansion into emerging markets reinforce its long-term growth potential.
A key pillar of Sony's strategy is its creative shift towards entertainment and content IP, prioritizing proprietary franchises and storytelling across multiple platforms. By leveraging its strengths in gaming, film, and music, Sony is deepening its focus on high-value intellectual property, integrating content across ecosystems to maximize engagement and monetization. This shift is evident in Sony's decision to spin off part of its financial segment in 2025 to prioritize entertainment and content creation, alongside increased investment in content, relative growth in its entertainment businesses, and strategic investments and acquisitions, reinforcing its competitive edge in the media landscape.
However, challenges such as technological disruptions, rising competition, and shifting consumer preferences require continuous innovation. By harnessing cross-segment synergies and expanding into emerging markets like EVs and digital content, Sony aims to sustain its leadership while deepening its focus on creativity, Kando, and long-term value creation.
Disclaimer: Please note that none of the information provided constitutes financial, investment, or other professional advice. It is only intended for educational purposes.